INDICATION and IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
JYNARQUE is indicated to slow kidney function decline in adults at risk of rapidly progressing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD).
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS LIVER INJURY
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS LIVER INJURY
- JYNARQUE® (tolvaptan) can cause serious and potentially fatal liver injury. Acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation has been reported
- Measure transaminases (ALT, AST) and bilirubin before initiating treatment, at 2 weeks and 4 weeks after initiation, then monthly for the first 18 months and every 3 months thereafter. Prompt action in response to laboratory abnormalities, signs, or symptoms indicative of hepatic injury can mitigate, but not eliminate, the risk of serious hepatotoxicity
- Because of the risks of serious liver injury, JYNARQUE is available only through a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy program called the Tolvaptan for ADPKD Shared System REMS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
- History, signs or symptoms of significant liver impairment or injury. This contraindication does not apply to uncomplicated polycystic liver disease
- Taking strong CYP3A inhibitors
- With uncorrected abnormal blood sodium concentrations
- Unable to sense or respond to thirst
- Hypovolemia
- Hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylaxis, rash) to JYNARQUE or any component of the product
- Uncorrected urinary outflow obstruction
- Anuria
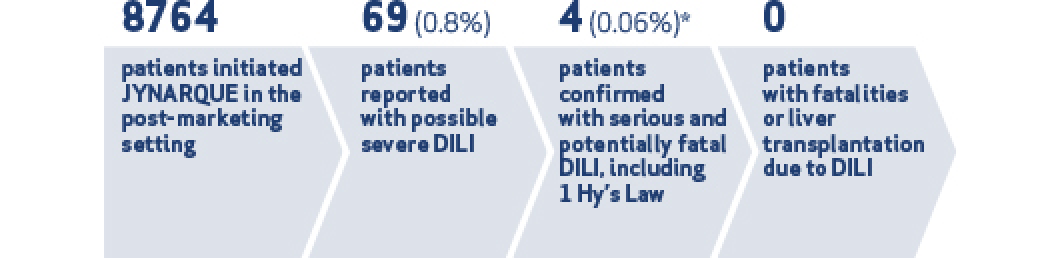
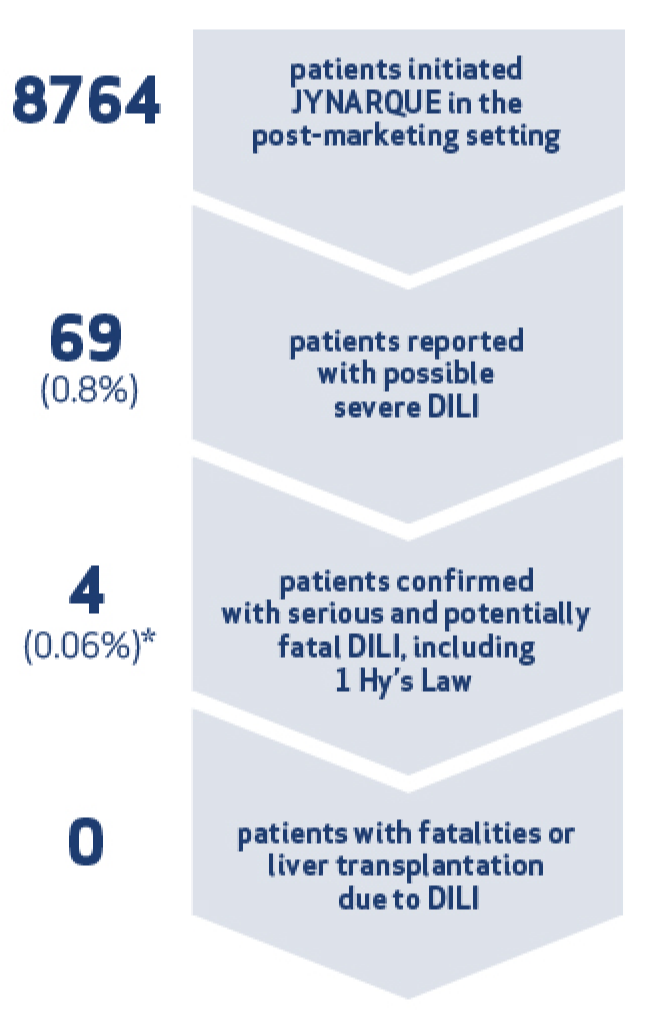
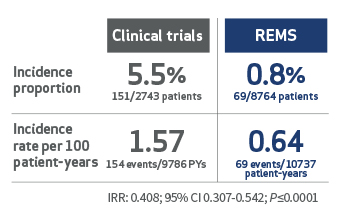
Serious Liver Injury: JYNARQUE can cause serious and potentially fatal liver injury. Acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation has been reported in the post-marketing ADPKD experience. Discontinuation in response to laboratory abnormalities or signs or symptoms of liver injury (such as fatigue, anorexia, nausea, right upper abdominal discomfort, vomiting, fever, rash, pruritus, icterus, dark urine or jaundice) can reduce the risk of severe hepatotoxicity. To reduce the risk of significant or irreversible liver injury, assess ALT, AST and bilirubin prior to initiating JYNARQUE, at 2 weeks and 4 weeks after initiation, then monthly for 18 months and every 3 months thereafter.
Hypernatremia, Dehydration and Hypovolemia: JYNARQUE therapy increases free water clearance which can lead to dehydration, hypovolemia and hypernatremia. Instruct patients to drink water when thirsty, and throughout the day and night if awake. Monitor for weight loss, tachycardia and hypotension because they may signal dehydration. Ensure abnormalities in sodium concentrations are corrected before initiating therapy. If serum sodium increases above normal or the patient becomes hypovolemic or dehydrated and fluid intake cannot be increased, suspend JYNARQUE until serum sodium, hydration status and volume status parameters are within the normal range.
Inhibitors of CYP3A: Concomitant use of JYNARQUE with drugs that are moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, lopinavir/ritonavir, indinavir/ritonavir, ritonavir, and conivaptan) increases tolvaptan exposure. Use with strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated; dose reduction of JYNARQUE is recommended for patients taking moderate CYP3A inhibitors. Patients should avoid grapefruit juice beverages while taking JYNARQUE.
Adverse Reactions: Most common observed adverse reactions with JYNARQUE (incidence >10% and at least twice that for placebo) were thirst, polyuria, nocturia, pollakiuria and polydipsia.
Other Drug Interactions:
- Strong CYP3A Inducers: Co-administration with strong CYP3A inducers reduces exposure to JYNARQUE. Avoid concomitant use of JYNARQUE with strong CYP3A inducers
- V2-Receptor Agonist: Tolvaptan interferes with the V2-agonist activity of desmopressin (dDAVP). Avoid concomitant use of JYNARQUE with a V2-agonist
Pregnancy and Lactation: Based on animal data, JYNARQUE may cause fetal harm. In general, JYNARQUE should be discontinued during pregnancy. Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with JYNARQUE.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. at 1-800-438-9927 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 (www.fda.gov/medwatch).
Please see FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION, including BOXED WARNING.